Economy of Hergom
The economy of Hergom spans a variety of economic sectors across Hergom.
Agriculture
History
Over the past three decades, Hergom's agricultural sector has significantly transformed to meet the growing needs of the Wolgos and now emancipated humans, both groups numbering over 260 million inhabitants. Prior to human emancipation, Hergom's agriculture was geared solely to meet the high protein needs of the Wolgos, with humans being left to subsistence farming in marginal lands and low-technology farming in the Phula and Alutea regions.
Three decades ago, the vast majority of agricultural output was directed towards producing animal feed, with minimal grains such as oats, rye, and wheat used for low-grade human rations. The Wolgos used the Bhrudhan and Peleykros regions to produce many of their non-animal-derived staples, such as root vegetables, oats, and other produce. Animal grazing was the cornerstone of Wolgos agriculture, with extensive ranching expanses producing large volumes of animal products. Slavery, though not a universal practice affecting all humans in Hergom, allowed the nation to focus predominantly on the needs of the Wolgos. Only the largely Gahnam and Chalam regions retained much of their traditional agricultural dynamism, albeit at subsistence and rustic levels, producing legumes and grains that are stable for these peoples.
The abolition of slavery and the introduction of paid labour for humans marked a significant turning point in Hergom's agricultural sector. This transition not only provided humans with purchasing power but also transformed them into significant commercial consumers. As a result, the market dynamics shifted, driving an industrial boom as newly empowered human consumers influenced the types of produce available and demanded a greater variety of products to satisfy their traditional diets.
With human consumerism now becoming a facet of the economy, there has been a substantial expansion of crop growing for human consumption and improvement in the efficiency of human held farmlands. The demand for a wider variety of grains, flours, and other products to meet human demands has led to a growth not only in farming of human staples but in a boom in food processing industries for human foods. Sorghum, millet, beans, peas and lentils which are staple grains for the Gahnam and Chalam communities, have seen a substantial rise in production. In 7689 alone, Hergom produced four million tonnes of sorghum and 3.8 million tonnes of millet. Wheat production in the Vatama highlands has also surged to meet the growing demand for non-wolgos bread amongst the human population.
The rapid increase in grain production has had beneficial side effects for Wolgos staples. The growing availability of wheat chaff and other grain waste has enabled the Wolgos to expand the fungi industry beyond forested areas into industrial facilities which have reduced their costs and grown the availability of fungi.
Livestock Farming Practices
Traditionally, pastoralism and ranching were key components of Wolgos agriculture that dated to the Bind and Old Dhonowlgos. These practices involved extensive grazing in expansive fields, where animals such as aurochs, pigs, boars and deer were raised in free range enviroments. Smaller animals such as hares and poultry were raised in small scale coups. However, the ever-increasing demand for animal products since the inception of Hergom, driven by the growing Wolgos population has lead for the past seventy years to the Wolgos adapting high intensity animal farming.
Factory farming in Hergom has replaced most traditional ranches and pastoral fields with large-scale industrial operations designed to maximise output. Tribal agroindustrial conglomerates have coallesed their members small holders into large cooperatives with syncronised practices and specialsation, Most small holders have transition away from grazing to growing high biomass yield varieties of buckwheat, rye, and giant tymothi grassto produce silage and feed for cooperative industrial animal pens.
Micro-livestock: The Wolgos have for milennia engaged in the rearing of arthropods and rodets as a source of protein, devoting extensive areas for copicing wood for grubs and reusing waste grain and sillage for rodents. Modern agroforestry practices use high growth varieties of willow to create giant copice plantations, producing a harvest every two years to supply the prefered source of feed Naesslor beetle grub farms. The Naesslor grubs, rich in protein, are no longer raised in wind driven and ventilated barns but in highly efficient warehouses with controlled climate and humidity for optimal growth and productivity. These grubs are typically harvested to be sold alive to consumers but practices such as chilling have become commonplace to meet the needs of the Wolgos population.
Grain spoilage of human farms, which was once considered waste, has found a new purpose in factory farming. Enormous mice and rat farms have been established to capitalize on this resource. Grain spoilage is used to feed these mice, which are bred and raised in high-density environments. Both adult mice and baby mice are popular food items for the Wolgos, who consider them a delicacy. Baby mice, in particular, are favoured as snacks, reflecting the diverse dietary preferences of the Wolgos population. Rat meat is typically mechanically recovered to produce patties and nuggets.
High-Density Livestock production: Most of the livestock in Hergom no longer comes from open fields but from countless of hectares turned to high-density pens. These pens are designed to house large numbers of livestock such as aurochs, pigs, boars and deer in high density confined spaces. The pens are often serviced by nearby sillage and feed farms who also benefit from the copious ammounts of manure produced. These farms are often reponsible for runoff pollution and algae blooms in the many rivers of Hergom. Sheds for poultry and a variety of other small animals are common, they are very large facilities feed by the same feed farms as other livestock.
Dairy Industry
Hergom's dairy industry stands as the largest in Gotha, producing an astounding four hundred million tonnes of milk anually. This volume accounts for almost sixty percent of the global milk production yet only a small portion is exported to Ombhrosdhom Commonwealth Treaty members. The Wolgos who have a strong preference for heavy and rich dairy products have develop dairy auroch varieties with a higher fat content making most wolgos milk comparable to light cream, The wolgos favor milk with fat content of atleast ten percent.
Although not dairy, blood products are considered part of the dairy industry as hey are harvested without killing cattle, aurochs are bleed at scheduled intervals to extract blood that is then stabilised and sold chilled for consumers to warm and consume.
In addition to fresh milk, Hergom's dairy industry processes large quantities of milk into a wide range of dairy products to satisfy the Wolgos market. The array of products includes yogurts, whey drinks, flavoured milk, kumis, creams, and cheeses. Each of these products caters to different tastes and culinary traditions of the Wolgos.
Yogurts and whey drinks are specially popular among the Wolgos. Whey is considered as refreshing drink to be drunk for hydration or as an alternative to water. Yogusts are seldomly sweetened with sugar, Wolgos fuit flavoured yogust are typically only sweetened by the fruits natural sugars and may seem a tad tart to human tastes.
Flavored milk has become a popular product, often flavoured with cranberries, strawberries, cucumber, chamomile, mint, passion fruit, banana or mango. The most popular flavours are those of temperate berriers, mint and tart passion fruit. The Wolgos find sweetened human yogurts and milks wholly unpallatable. Kumis, a fermented dairy drink, is also produced in large quantities. Kumis has a slightly alcoholic content that is often fortified with distilled grain spirit to produce a highly alcoholic and popular version.
Creams, butter and cheeses are essential components of the Wolgos diet. The high-fat milk used in their production results in rich, flavorful creams and a wide variety of cheese. The wolgos produce soft cheeses and frsh butter along with more robust aged cheeses and fermented butters, they are partial to aging cheese with molds and with maggots.
Animal Welfare
The high dependence on animal products and the efficiency of the livestock industry in Hergom have come at a significant cost to animal welfare from a human perspective. The Wolgos, given their unique psyche, treat animals in a purely instrumental manner. As such, Wolgos livestock farms can be nightmarish by human standards. The Wolgos are unconcerned with the perceived welfare of animals, focusing solely on maximising productivity.
Abattoirs in Hergom, while providing comparatively modest wages, are romanticised as desirable jobs for younger adult Wolgos men. The Wolgos in these jobs typically relish the killing of animals and see it as form of entertainment, making it one of the jobs with highest workr satisfaction.
Foreign animal rights organisations that have witnessed Wolgos abattoirs are appalled by the sadistic enjoyment Wolgos workers appear to take in their roles, and by the the harsh conditions animals endure in most indistrial farms. The treatment of animals in these facilities is often brutal, with little regard for their suffering but foreign concerns are largely incomprehensible to the Wolgos.
United Agricultural Policy
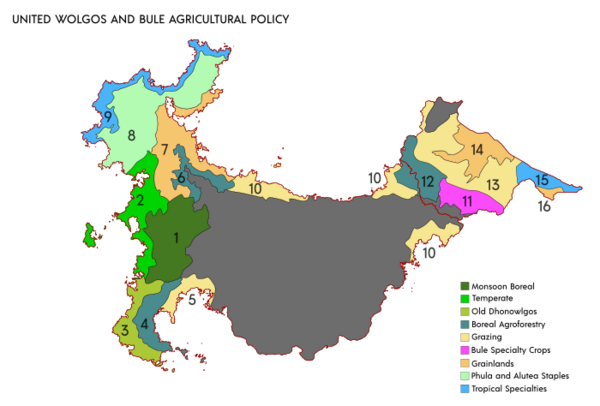
The Ombhrosdhom Commonwealth Treaty organisation is working on synchronising its members' agricultural policy. To date, only Bule has achieved policy parity with Hergom, and mutual agricultural output is complementary to reduce redundancy, costs, and waste and increase profitability. The territories have been split into specific regions with tailored policies and agricultural specialisations best suited to the climate, geology and hydrology.
1- Wodranis Moonsoon Boreal Region
The heartland of Hergom is a large boreal expanse with a large river network formed by the Wodranis River and its tributaries. The once completely forested region is known for its high rainfall, with at least an hour's worth of rain every day. In summer, the moist winds from the Asherian seas bring heavy and near-constant monsoon downpours, while in the winter, a drier climate brings heavy snowfall.
This region has a complex layout of forest corridors, thinned-out grazing forests, and immense fields dedicated to rye, oats, buckwheat, and giant timothy grass. Eighty-five per cent of vegetable output is for silage and animal feed. Between large farm expanses, there are massive complexes holding millions of aurochs and other livestock in high-density pens and sheds for industrial-scale meat and dairy production.
The remaining vegetable output is grain for Wolgos needs, such as aged breads, spirits and porridges. Tubers like potatoes, carrots and other root vegetables are popular crops. Greenhouse farming has steadily grown in popularity as nuclear power has allowed the extensive and cheap heating of greenhouses.
The thinned-out forests and forest corridors prevent the fragmentation of forest cover, which is vital for the timber industry and industrial game meat production. These forests also produce berries, fungi and honey.
The river network produces fish and feeds numerous bogs and flooded fields for the production of waterlogged crops such as cranberries.
2 - Lendhmos-Peleykros Temperate Corridor
This zone is less rainy than the Wodranis region, yet its renouned for its frequent light showers, lightning storms and fog banks across fields and coasts. The zone has ample water resources, gentle hills and flat plains that once were thickly forested.
Much of the region is used to cultivate root vegetables, leafy greens, legumes, cucumbers, and other common Wolgos vegetables. Wheat and rye are commonly grown for the production of Wolgos-style breads and flours. Oil in the form of rapeseed is commonly produced here, as are fruits such as apples, pears, berries and many others.
The main forms of sillage produced are clover, alfalfa, and legumes, mostly for cattle and poultry farming. Willow copicing is common for Naeslor grub production.
The coast of this zone is largely devoted to industrial rope kelp farms that extend to the horizons of the production of biodiesel, with only deeper waters devoted to fish and krill farming. Krill farming and minnow farming are essential phosphate sources when processed as fishmeal for the production of fertilisers.
3 - Bhrudhan Old Dhonowlgos Heritage Territory
Bhrudhan is a temperate and less rainy region of the new Wolgos homeland of southern Kupeya. The zone is being developed to resemble much of old Dhonowlgos in architecture and farming without preventing the growth of more modern agricultural concerns. The land ownership and management strategy of the region is designed to promote the cooperatives of many smallholder homesteads and estates, with old Dhonowlgos-style villages developing adjacent cooperative storage silos, warehouses and machinery storage and rental depots.
The region is developing to produce the highest quality Wolgos produce, meats, and processed foodstuffs. The region's products earn a premium due to their focus on quality and traditional practices. Geese and other poultry are renowned, as are the wool products and other woollen fabrics produced in the region.
More modern concerns centre around luxury products such as flowers; the region has extensive flower greenhouses that feed the national demand. Wolgos cream spirits of high quality are produced from potatoes and wheat, with refined clear spirits once deemed for Eokoesr use. They are now sold to Wolgos consumers who yearn for the glorious past.
4 - Dheghom, 6 - High Vatama, 12 - Dharian Agroforestry zones
Dheghom is a subregion of Bhrudhan that has a slightly different agricultural policy. Its focus is the industrialisation of virgin forests for both replenishable timber and industrialised game meat production. Nevertheless, there are an ample number of old-style Wolgos villages and farms expanding in the region.
Industrial game forests are meticulously preserved and engineered to maximise the reproduction and survival of game animals such as boars, deer, grouses and others. These are sustainably thinned to produce large amounts of high-quality game meat that is in high demand by consumers. To increase profitability, the region excels in forest beekeeping, fungi farming and wild berry growing. Hunting tourism is another growing activity, with tourists enjoying a plethora of resorts and hunting refuges.
High Vatama and Dharian agroforestry regions are much like Dheghom but with a much higher human presence and economic participations. Human cooperatives have been formed to supply Wolgos tribal conglomerates with timber, turpentine, resins, dyes, and other forest products. High Vatama Chalam cooperatives have innovated new techniques for cheap mass production of timber-like products; the Chalam grow fast-growing bamboo and compress flattened bamboo rods into planks and beams bonded by resins to produce cheap timber-like construction materials for the hungry construction industry.
5 - Ghelwrada Grazing Zone
The Ghlwarada grazing zone covers much of the Dhgwhitstanos Weikosa. a region wholly composed of deep taiga and tundra. The lowly populated region only has fishing, seabird farming, and reindeer herding as agricultural activities. There are some small-scale enterprises setting up greenhouses that take advantage of geothermal power to produce fresh produce for the local Wolgos settlers.
Wolgos families earning a living from reindeer herding typically live in large mobile homesteads the size of mining dump trucks, forming self-contained communities dedicated to meat production and Haiter raising for ornamental and ceremonial activities.
Small villages along the icy coast dedicate themselves to high oil-content fish and other cold-water fish for Wolgos and human consumption. Shellfish are another economically important product of the region.
7 - Vatama Grainlands
The Vatama grainlands is a multi-region zone with a policy geared toward the production of wheat, oats, corn and non-flood rice. The regions are largely flat save for Vatama itself which is hilly and requires extensive terracing. The current quotas split evenly production between fooder, animal feed and half for human consumption. Vatama produces high-quality wheat and other flours for the Chalam and Gahnam markets, products which have greatly improved food security and quality for these human subjects who now can enjoy their traditional high cuisines and ample access to ready-made foodstuffs.
Of the animal feed produced, ten per cent is reserved for raising poultry and goats for human consumption, while the rest is exclusively reserved for Wolgos livestock.
8 - Phula-Alutea Staples Territory
The Phula-Alutea Staples Territory lies in the Chalam and Gahnam heartlands of Hergom. These regions are largely populated by humans with minority Wolgos populations. These are subtropical regions with variable rainfall and typically drier summers. They have grown in agricultural importance since human emancipation as investment flows into the region.
For the Wolgos, the regions are important for the production of cotton, oil crops, sugar cane for biodiesel, coffee, and tea, as well as spices and fruits.
The region was largely subsistence and had marginal tradable surpluses, but high investment in the past few decades had led to the industrialisation of human-leased lands and the formation of wholly human cooperatives.
Around eighty per cent of all edible crops are grown for human consumption. They largely include a large variety of pulses, millet, sorghum, rice, corn, vegetables, cassava, sweet potatoes and spices.
Human cooperatives dedicated to the production of cotton have seen dramatic rise in production and investment as they increase volumes and feed the textiles industry.
9 - Northern Tropical Band
The northern band is the slim region in Hergom, mostly populated by humans, which has seen long-term investment for the production of high-value tropical cash crops such as coffee, fruit, timber, taro and a wide variety of cash crops of value for the Wolgos market. Once dependent on slavery, it is now home to vast swathes of company towns run by tribal Wolgos conglomerates to maintain a paid human workforce and profit from the human workforce.
10 - Sterpleudha Grasslands, Dhaadhii and Waringa territories
They are relatively new agricultural regions, mostly boreal and dedicated to cattle and sheep grazing. Producing meat, leather, tallow, dairy, butter and wool. These regions have large Shriaav settlements as they sought virgin land to create some distance between themselves and the Wolgos. The Wolgos themselves only account for ten per cent of the region's population, with most being Utura humans. The Wolgos reversed the Second Coalition War policy towards the Utura and invested in the reconstruction of their traditional settlements and their traditional economic practices with modernised techniques and supplies.
The old Utura city of Motos has been reconstructed and has seen investment to transform it into an economic hub.
The Utura were traditionally forest farmers and herders and have been encouraged to form cooperatives to increase their participation in the meat and dairy industry.
11 - High Inaja highlands
The once distant and dry highlands of the Inaja have grown into an important economic region of Bule since its alignment with Hergom. The region is the only wine-producing region of Tzeraka and Kupeya. The region produces largely fruity reds and dry full-body reds, with the best vintages being produced in the last decade. The Bule Aldsegians have been successful in promoting wine consumption as a luxury practice. Red wine, despite being a human drink, does not make the Wolgos feel ill as it is low in simple carbohydrates, and they thoroughly enjoy the wine's complex flavours and acidity.
The region is also renouned for its citrus groves producing much of the united agricultural policy domain oranges, lemons, mandarins and other citruses.
13 - Musi-Inaja Grasslands
The vast Aldgesian dominated ranching estates producing copious quantities of beef.
14 - Umojio River Grainlands
The Umojio River grainlands are almost entirely dedicated to grain production in the form of wheat, corn and oats. They also produce legumes, sunflower seeds, and oils. A region is so big that it exports much of its harvest to other nations in Tzeraka and in the Wolgos sphere of influence. Its river networks necessitate careful management for irritation due to the drier and semi-arid qualities of the region.
15 - Lephoo Cashcrops Territory
A region much like the Northern Tropical Band but with Aldgesian and Birizy dominance. Largely dedicated to bananas, plantains and tropical fruits.
16 - Outer Dharian Specialty Zone
The highlands with an oceanic and continental climate, Anarian fruits and olives are grown in this region. Bubale olives being the only variety available for consumption in Hergom and much of their sphere of influence.
Energy
- Main article: Energy production in Hergom
Hergom's approach to energy production is characterized by large-scale industrial efforts that prioritize economic growth and energy efficiency over environmental preservation. The biogas industry relies heavily on expansive fields of giant kelp, which cover millions of hectares along the coast. These fields are meticulously managed by agricultural rigs, leading to significant ecological disruption. The continuous harvesting of kelp for methane production not only depletes underwater flora and fauna but also generates nutrient-rich waste, causing harmful algae blooms. These blooms create hypoxic conditions that suffocate marine life, demonstrating the Wolgos' disregard for the coastal ecosystem in favor of industrial advancement.
In addition to biogas, Hergom has developed a robust nuclear industry, initially focused on weapons production but now significantly diversified into civilian energy production. Thorium, preferred over uranium for its safety and sustainability, powers the country's major nuclear plants, such as the Gelwathra power plant, which produces 32 gigawatts of energy. This nuclear capacity supports a wide range of applications, including small reactors for high-reliability train engines, enhancing transportation across Hergom. Despite adhering to the non-proliferation treaty, the Wolgos maintain a strong focus on nuclear weapons production, ensuring their defense capabilities remain formidable.
Hydroelectric power also plays a crucial role in Hergom's energy strategy, with thousands of dams across the country harnessing the extensive river networks and mountainous valleys. The largest projects, like the Kildhra Dam, generate vast amounts of electricity but at significant environmental and social costs. The diversion of rivers such as the Haratovana has led to severe ecological disruption and the collapse of local agriculture, particularly affecting neighboring regions like Mantharavati. The combined impact of these energy production methods underscores the Wolgos' relentless pursuit of industrial growth, often at the expense of environmental sustainability and the well-being of affected human communities.
Mining
- Main article: Natural resources of Hergom
Heavy manufacture
Light industry
Technology
Services
- Main article: Media in Hergom
