Hergom ep swekorwos
| Hergom ep Swekorwos Hergom ep Swekorwos | |
| Flag | Coat of arms |
|---|---|

|

|
| Motto: "At the world's very edge, where horizons meet the sky, We rise for our last stand, as the stars bear witness on high. Blood heralds our era, as old tales are undone, For an everlasting dominion, that shall eclipse even the sun." | |
| Anthem: | |
| Locator map | |
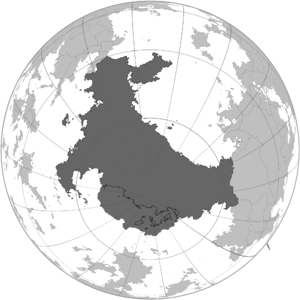
| |
| Capital city | sample_city |
| Largest city | Ombhrosdhom |
| Official language | Wolgos language |
| Other languages | Chala |
| Ethnic group | |
| Religion | 53% Dlroch'veldr
15% Nara Akchacknism 15% indigenous beliefs 13% Venara Akchacknism 4% Neo-Shuocian |
| Demonym(s) | Herg |
| Government | |
| Government Type | Unitary Tribal Federation |
| Your 1st leader title (e.g. King) | President Name |
| Your 2nd leader title (e.g. Prime minister) | Vice President Name |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Establishment | |
| Area | |
| Total | 33,082,896.19 km2 |
| Water % | 4.66% |
| Population | |
| Total | 257,345,233 |
| Density | 7.78/km2 |
| Economy | |
| Economy type | Capitalist |
| Currency | Uhum () |
| Development index | 0.920 |
| Other information | |
| Time zone | All time zones |
| Driving side | Left |
| Calling code | +09999 |
| Internet code | -X00900 |
The premier Wolgos nation in Gotha, known as Hergom ep Swerkorwos, is situated in the deep south of the planet. It encompasses the entire region of Kupeya (called Khrupeva by the Wolgos), which includes the South pole, as well as the southernmost part of Tzeraka (called Therakha by the Wolgos). The nation recently celebrated its centenary anniversary, marking the foundation of the state after the dissolution of the Bind and Dhownolgos. Its establishment followed the conclusion of the Pan Oceanic War and the subsequent Second Great Wolgos Trek.
Despite its extensive land area, Hergom ep Swerkorwos primarily experiences challenging climates. Only around fifteen percent of its territory enjoys a temperate climate, while the remaining land is divided into alpine, taiga, tundra, and varying degrees of harsh arctic climates.
The governance of Hergom ep Swerkorwos departs from the monastic and theocratic systems of its predecessors. Instead, the nation is administered by a federated cabal of Wolgos tribes. While tribes often dominate significant stretches of territory, no Weikosa (region) is monopolized by any particular tribe. Tribes are recognized as legal entities with extraterritorial authority, representing the Wolgos and their human subjects. They encompass numerous clans and families, providing economic, legal, and welfare support.
The state does not provide comprehensive welfare services. Instead, the responsibility for healthcare, education, legal aid, security, and economic assistance lies with the tribes. The level of services varies among tribes and is often tied to their economic influence. Wolgos tribe members frequently work in their respective tribes' expansive enterprises or establish businesses associated with their tribe. However, it is not uncommon to find Wolgos working for tribes other than their own, effectively becoming adoptive members of the tribe they collaborate with.
Cities in Hergom ep Swerkorwos are vibrant hubs where diverse tribes cooperate to conduct efficient business. However, conflicts and hostile competition can arise. The government serves as a pseudo tribe composed of representatives from all tribes, working to harmonize relations and maintain a regulatory and legal framework that supports efficient industry and business operations throughout the nation.
While tribes handle most internal affairs, the government retains control over defense, monetary policy, currency minting, the legal system, relief efforts, intelligence operations, and foreign policy. Defense, infrastructure investments, and intelligence comprise the largest government expenditures. To fund its operations, the government imposes a percentage of revenue and various taxes and fees on the tribes for the services it provides.
As part of its foreign policy, the government exercises control over a number of sorikwentom (corporations and associations). Some of these entities are known to oversee twenty-seven major criminal networks across Gotha. These corporations engage in illicit activities such as distributing drugs, arms manufactured in Hergom, and a range of other illegal operations. The significant profits generated from these activities contribute to Hergom's foreign currency reserves.
Etymology
"Hergom ep Swekorwos" can be interpreted as "Enduring Strength at the World's End" or "Resilient Power at the Edge of the World." It conveys the idea of a powerful and enduring Wolgos nation located in a remote and distant region.
7598 - 7603 Wolgos Scourge (20's to early 30's tech leap) 7603 - 7620 Second Wolgos Trek 7608 Foundation of hergom
History
- See also: Dhonowlgos
- See also: The Bind
- Main article: History of Hergom
Pre-Wolgos History
Kupeya's history is marked by limited development due to its harsh environment. The northern coast had temperate land, but the variable climate rendered the colder interior inhospitable. Modest Chalam princedoms emerged along the coast, subsisting on farming and trade with the Raian archipelago. Inland, there were hunter-gatherer villages and trading communities by rivers. The advanced Phula and Alutean peninsula had stone temples and fortified villages. Alutea's progress stood out due to Ithrien's colonial influence. Kupeya's isolation was shaped by its polar proximity and the Raian archipelago, known for its rainforests, trade, and piracy. Despite bordering Kupeya, dense rainforests deterred colonization unlike neighboring regions.
7603 - 7620 - Second Wolgos Trek

After the Wolgos Scourge, Kupeya underwent a significant transformation known as the Second Wolgos Trek. The Peleykros peninsula became a hub for Wolgos migrants, reshaping the region.
Following the devastation, the Bind navy orchestrated a massive migration, relocating people and machinery from Altaia. They collaborated with Kamura and others, despite facing financial ruin. The arrival of the first Wolgos on Kupeya's shores left a handprint emblem, now on the nation's flag, commemorating the event.
Around forty million Wolgos and three million Shriaav were transported from Altaia to Kupeya over fifteen years, a complex logistical operation. However, eight million Wolgos remained in Altaia, and two million dispersed across the Shangti region, May of whom have migrated to Hergom in the subsequent decades.
Initially, challenges arose in Kupeya due to clashes with locals and limited resources. Import reliance decreased, pushing the Wolgos to adapt. The Wodranis river plains became pivotal, providing sustenance through native wildlife and the use of the indigenous population as food.
Infrastructure developed, with fishing ports and docks along rivers established by the remaining Bind administration. These developments supported settlements and resource transportation to Ombhrosdhom, evolving into a thriving city during Kupeya's transformation.
7608 Foundation of Hergom ep Swekorwos
7632 - 7634 First Coalition War
7663 - 7664 Second Coalition War
7664 - First use of nuclear weapons in Ephesus Front by the Coalition
7664 - End of the Second coalition war
7665 - Establishment of the Tzeraka demarcation border
7672 - First Wolgos nuclear Test
7681 - Non-Proliferation Treaty
7689 - Current Era
Geography
Government
Justice and Law
Theory
Criminal Theory
At the heart of the Wolgos legal framework lies a strategic approach, a reflection of their innate psychopathic tendencies. For the Wolgos, crime is not solely an act that disrupts social harmony but rather one that upends the delicate balance of power and authority. Actions that threaten the interests of the state, society, tribe, or influential individuals are marked as criminal, mirroring their stratified society where not all Wolgos are equal in the eyes of the law.
However, the determination of what constitutes a crime isn't solely rooted in strategic considerations. Established Wolgos norms, often intertwined with religious dogma, play a significant role in shaping the boundaries of acceptable behavior. The teachings of Dlroch'vlder serve as a moral compass, guiding the complex interplay between morality and strategic considerations.
The Wolgos, though not innately collectivist, have developed a strategic collectivist perspective through their evolution within larger and more intricate societies. Adhering to established moral norms has become crucial as they navigate these complexities. Dlroch'vlder's teachings provide a shared ethical foundation, allowing the Wolgos to construct a unique sense of morality in the midst of shifting power dynamics.
Within Wolgos society, a notion of general rights and expectations for the Wolgos alone exists, though tinged with nuances. Equality isn't uniform; instead, a spectrum of equality prevails, where certain individuals are inherently more equal than others. This hierarchy aligns with the strategic nature of their society, where power and influence intricately shape the definitions of right and wrong.
It's important to note that these intricacies may not seamlessly apply to interactions with humans. The Wolgos moral code, intricately woven into their psyche, might not readily translate to human norms. What's deemed a crime or moral transgression in their society may lack translation or comprehension when projected onto human behaviour.
Judicial theory
The concept of justice among the Wolgos differs significantly from that of humans, as their understanding revolves around the notions of harmony and continuity rather than equity and righteousness. Retributive or punitive justice does not serve as the guiding principle for Wolgos justice; instead, they gravitate toward what can be termed as strategic justice.
Interestingly, most actions that may be perceived as crimes are addressed through restorative justice practices, with the aim of restoring collective balance and harmony. The well-being of collective interests takes precedence over the individual's injury. The extent and involvement of restorative practices are highly contingent on the influence wielded by individual Wolgos, their kin, or their tribe. Lone individuals without a close social collective or those of low standing and influence often find themselves at a disadvantage and face significant punitive risks.
Within Wolgos societies, there is no impetus to address power imbalances that disadvantage isolated or low-standing individuals. This is primarily because doing so would diminish the influence and degree of impunity that families, clans, and tribes can leverage. Furthermore, this system of justice serves as an important social mechanism that helps the Wolgos overcome potentially antisocial tendencies. It fosters the need for cooperation and the stability of family, clan, and tribal structures, thereby ensuring the stability of the state itself.
One disadvantage of this system, from a human perspective, is the vast disparity in how crimes are punished or resolved. Grave crimes can go unpunished if influential or powerful individuals exercise significant impunity, particularly if the injured party holds little social capital or importance. Individuals of low standing or social capital can face insurmountable obstacles to justice and are at high risk of exploitation or harm.
It is worth noting that the state is the only party that can achieve complete restitution if injured. Charges brought by the state are usually challenging to dispute, as a crime against the state is seen as a crime against Wolgos kind. Nevertheless, there are checks and balances in place, as they are in the best interest of the state. Wolgos societies can engender a collective sense of paranoia if they perceive the interests of tribes to be threatened.
Collective Accountability
Accountability can extend beyond individual responsibility to include collective accountability. Clans or tribes can be held responsible for the actions of their members, fostering a sense of collective responsibility and encouraging internal mechanisms for addressing conflicts and ensuring compliance with community norms.
Administration of justice
The judicial system of Hergom, a sprawling domain defined by its intricate societal fabric, operates through a three-stage framework that blends age-old traditions with contemporary adaptations. With an emphasis on harmonious resolutions and the preservation of collective well-being, this system navigates disputes through mediation, court arbitration, and appellate review.
Restorative Justice - Mediation Pathway
At the core of Hergom's legal philosophy lies a profound commitment to restorative justice. Grounded in the decentralized nature of its judicial structure, the system places mediation and reconciliation at the forefront of dispute resolution. Conflicting parties are granted the opportunity to seek common ground through negotiation, facilitated by skilled and accredited mediators. The primary objective remains the restoration of harmony and cohesion, with punitive measures taking a back seat.
Mediation occurs within various settings, ranging from dedicated mediator chambers to mutually agreeable locales. To formalize resolutions, notaries and witnesses often preside over the final stages.
The Court for Dispute Resolution
Should mediation's path prove impassable, disputes find their way to the courts for arbitration by a qualified judge. This phase carries with it specified taxes and hourly charges, necessitating meticulous preparation by all involved parties. The involvement of mediator representation is strongly recommended, lending an expertise to the proceedings. Drawing from a blend of state and tribal customary laws, the courts administer justice within their respective communities.
It is important to note that the courts' realm extends beyond mere disputes. Individuals facing charges initiated by the state or law enforcement entities often find themselves in the initial embrace of the court. However, even in these circumstances, mediation remains the preferred avenue, aiming to foster a resolution between the accused and the state. Should this pursuit fall short, the court's role is activated, with the accused bearing the onus of any relevant fees and hourly expenses.
Courts of Appellate Review
Dissatisfied parties or individuals may seek recourse through the courts of appellate review, provided legal provisions permit. Yet, this path to redress is not devoid of considerations. The pursuit of appellate review entails financial implications, often necessitating collateral commitments. Appellate courts stand as a platform to scrutinize lower court decisions, rectifying errors or rights violations.
Judicial Debt
In Hergom, the path of justice intertwines with fiscal responsibility through the concept of judicial debt. As legal proceedings unfold, financial obligations emerge for parties involved. Those unable to meet these commitments face a meticulous process of debt recovery, which may involve asset liquidation. Tribes, essential to Hergom's social fabric, can also be called upon to share the burden of settling debts. Should conventional measures falter, the judiciary can impose sentences of labor benefiting the state or earnings garnishing.