Negasi: Difference between revisions
m (→Waterways) |
m (→Geography) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| Anthem = <br />Our Beautiful Homeland <small>(''Kyawawan Qasarmu'')</small> | | Anthem = <br />Our Beautiful Homeland <small>(''Kyawawan Qasarmu'')</small> | ||
| anthem link = | | anthem link = | ||
| map = Negasi.png | | map = Negasi locator.png | ||
| capital city link = Bogaye | | capital city link = Bogaye | ||
| capital city = Bogaye | | capital city = [[Bogaye]] | ||
| largest city = Elmisi | | largest city = Elmisi | ||
| official language link = Negasi language | | official language link = Negasi language | ||
| official language = Negasi | | official language = {{wp|Hausa language|Negasi}} | ||
| other languages = Liloba, Koloba | | other languages = Liloba, Koloba, Auresian | ||
| Ethnic group = [[Balisubri]], [[Baloma]] | | Ethnic group = [[Balisubri]], [[Baloma]] | ||
| ethnic groups = | | ethnic groups = | ||
| Religion = [[Naskel]], [[Anur]] | | Religion = [[Naskel]], [[Anur]] | ||
| Demonym = Negasi | | Demonym = Negasi | ||
| government type = Unitary parliamentary semi-presidential republic | | government type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|semi-presidential republic}} | ||
| Leader 1 title = Grand Chief | | Leader 1 title = Grand Chief | ||
| leader1 = [[Rakanja Sadaka]] | | leader1 = [[Rakanja Sadaka]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| internet code = .neg | | internet code = .neg | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Negasi''', officially the '''Negasi Republic''' ({{wp|Hausa language|Negasi}}: ''Jamhuriyar Negasi''), is a country predominantly in southwest [[Tharna]] with a portion in northwest [[Tzeraka]]. Its western boundary is the [[Vovodaran Sea]] and the [[Tanga Moji Sea]] lies to the country's east. The [[Ubani Canal]] links these two seas, forming a route for ocean-going vessels between the [[Ovestan Ocean|Ovestan]] and [[Phasian Ocean]]s. The country has an area of {{cvt|1,217,757|km2}} with a population of 88,910,846. | |||
'''Negasi''', officially the '''Negasi Republic''' ({{wp|Hausa language|Negasi}}: ''Jamhuriyar Negasi''), is a country predominantly in southwest [[Tharna]] with a portion in northwest [[Tzeraka]]. Its western boundary is the [[Vovodaran Sea]] and the [[Tanga Moji Sea]] lies to the country's east. The [[Ubani Canal]] links these two seas, forming a route for ocean-going vessels between the [[Ovestan Ocean|Ovestan]] and [[Phasian Ocean]]s. The country has an area of 1,217,757 | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{main|History of Negasi}} | |||
===Early history=== | ===Early history=== | ||
===Four Councils period=== | |||
===Colonial period=== | ===Colonial period=== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
The region was colonized by [[Auresia]] in the early 7400s, with the first records of the South Tharnan colony dating from October 5, 7407. | The region was colonized by [[Auresia]] in the early 7400s, with the first records of the South Tharnan colony dating from October 5, 7407. | ||
During the colonial period, the Ubani Canal was built. Construction began in 7563 and the canal opened to ship traffic on December 15, 7607 after some delays during the [[ | During the colonial period, the Ubani Canal was built. Construction began in 7563 and the canal opened to ship traffic on December 15, 7607 after some delays during the [[Wolgos Scourge]]. | ||
=== | ===Contemporary period=== | ||
Rising anti-colonialism globally after the turn of the 77th century led to a rise in Negasi nationalism in the 7600s. The formation of the [[Open Seas Security Organization]] (OSSO), with its purpose of fostering maritime trade, after the [[First Coalition War]] (7632-7634) underscored the importance of the canal for shipping and as a national resource. A general strike occurred across much of Negasi beginning on November 16, 7633. Among other effects, the strike shut down canal operations, preventing ship transit between the Ovestan and Phasian Oceans. The strike led to Auresia granting Negasi its independence on January 30, 7634 in exchange for the restarting of canal operations and a promise to keep the canal open. | Rising anti-colonialism globally after the turn of the 77th century led to a rise in Negasi nationalism in the 7600s. The formation of the [[Open Seas Security Organization]] (OSSO), with its purpose of fostering maritime trade, after the [[First Coalition War]] (7632-7634) underscored the importance of the canal for shipping and as a national resource. A general strike occurred across much of Negasi beginning on November 16, 7633. Among other effects, the strike shut down canal operations, preventing ship transit between the Ovestan and Phasian Oceans. The strike led to Auresia granting Negasi its independence on January 30, 7634 in exchange for the restarting of canal operations and a promise to keep the canal open. | ||
| Line 62: | Line 64: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
While predominantly located in Tharna, Negasi is astride the division between Tharna and Tzeraka, with a portion of the country's southwest located in the latter continent. The Vovodaran Sea lies to the west and the Tanga Moji Sea adjoins Negasi's east coast. The | While predominantly located in [[Tharna]], Negasi is astride the division between Tharna and [[Tzeraka]], with a portion of the country's southwest located in the latter continent. The Vovodaran Sea lies to the west and the Tanga Moji Sea adjoins Negasi's east coast. The Koradum Mountains lie along a significant portion of Negasi's northwestern border. This region, the [[Negasi highlands]], comprises nearly a third of Negasi's area and is home to three large lakes: Moto, Jelwa, and Tila. The Giganum Mountains are in the south. The Ubani Narrows lies between the two large mountain ranges. | ||
The Oluwa Islands comprise a series of several islands off Negasi's west coast in the Vovodaran. There are several islands in the Tanga Moji, including Jabar, Set, Moriba, Salanko, M’basso, Torosso, Kolibelo, and Dyalinko islands. | The Oluwa Islands comprise a series of several islands off Negasi's west coast in the Vovodaran. There are several islands in the Tanga Moji, including Jabar, Set, Moriba, Salanko, M’basso, Torosso, Kolibelo, and Dyalinko islands. | ||
===Waterways=== | ===Waterways=== | ||
{{ | {{see also|Ubani Canal}} | ||
Over 500 rivers course through Negasi and many serve as sources of {{wp|hydroelectric}} power. While most have limited navigability, a few are navigable. In particular, the Babukar River is suitable for ocean-going vessels for nearly a hundred kilometers, and even further with dredging. As a result, the river is the primary waterway for the [[Ubani Canal]] which was constructed during the latter half of the 76th century. The canal's total route is 816 km | Over 500 rivers course through Negasi and many serve as sources of {{wp|hydroelectric}} power. While most have limited navigability, a few are navigable. In particular, the Babukar River is suitable for ocean-going vessels for nearly a hundred kilometers, and even further with dredging. As a result, the river is the primary waterway for the [[Ubani Canal]] which was constructed during the latter half of the 76th century. The canal's total route is {{cvt|816|km}}, connecting the Ovestan Sea to the Phasian Ocean, using the Ouahika River for the canal's western-most segment. | ||
At over 684 km | At over {{cvt|684|km}}, the Babukar is Negasi's longest river. It is navigable for about two-thirds of its length, with the Ubani Canal route using the river for {{cvt|338|km}}. The western portion of the canal route uses {{cvt|196|km}} of the Ouahika River. The Déda, which flows into the Babukar, shares {{cvt|149|km|1}} of its {{cvt|256|km}} with the canal. Other significant rivers include the Effingo, Nyale, Sassasam, Missiam, Télo, Sary, N'goulabéri, Ababéri, Cana, and Wukari. Although each is navigable for portions of their course, they are not navigable by ocean-going vessels. | ||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
{{main|Government of Negasi}} | |||
The Negasi Republic is a {{wp|unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|semi-presidential republic}}. The {{wp|head of state}} is the grand chief who is chosen by {{wp|direct election}} to fill a five-year term. The superintendent is the {{wp|head of government}} and is typically the leader of the majority party in the Superior Council, Negasi's {{wp|parliament}}. The superintendent serves until removal through a vote of no confidence or another party becomes the majority party in the Superior Council. [[Rakanja Sadaka]] serves as grand chief and [[Ayubu Owethu]] is the current superintendent. | The Negasi Republic is a {{wp|unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|semi-presidential republic}}. The {{wp|head of state}} is the grand chief who is chosen by {{wp|direct election}} to fill a five-year term. The superintendent is the {{wp|head of government}} and is typically the leader of the majority party in the Superior Council, Negasi's {{wp|parliament}}. The superintendent serves until removal through a vote of no confidence or another party becomes the majority party in the Superior Council. [[Rakanja Sadaka]] serves as grand chief and [[Ayubu Owethu]] is the current superintendent. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 87: | ||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
The Negasi National Guard serves as the country's armed forces. It has a land guard, maritime guard, and an air service. The full-time professional force is relatively small but all citizens through age 30 are considered reserves and may be called up in the event of a national emergency. | {{main|Negasi National Guard}} | ||
The [[Negasi National Guard]] serves as the country's {{wp|military|armed forces}}. It has a land guard, maritime guard, and an air service. The full-time professional force is relatively small but all citizens through age 30 are considered reserves and may be called up in the event of a national emergency. | |||
===Administrative divisions=== | ===Administrative divisions=== | ||
Negasi is a unitary state, so its administrative divisions have limited authorities of their own. The first-level divisions are the four quadrants: Bakin-kogi, Tsaunuka, Tumkarik, and Masokudo. Each is overseen by a high chief and high council. Each quadrant has a number of ''kasashe'' (lit. lands) of which there are a total of 96. A chief and council preside over the functions of the ''kasa''. Considered on an equal level, cities, towns, and villages represent local governance under the administration of their local chief and local council. The chiefs at each level are | Negasi is a {{wp|unitary state}}, so its administrative divisions have limited authorities of their own. The first-level divisions are the four quadrants: Bakin-kogi, Tsaunuka, Tumkarik, and Masokudo. Each is overseen by a high chief and high council. Each quadrant has a number of ''kasashe'' (lit. lands) of which there are a total of 96. A chief and council preside over the functions of the ''kasa''. Considered on an equal level, cities, towns, and villages represent local governance under the administration of their local chief and local council. The chiefs at each level are appointed by the chief and confirmed by the council of the next higher level. Citizens directly elect members of the local council. The local councils in turn elect the members of the council in each ''kasa''. The ''kasa'' councils elect members of the high council. | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| Line 98: | Line 102: | ||
The [[Negasi nauyi|nauyi]] (lit. weight), with the symbol ₦, is the country's currency. The nauyi is divided into 100 dari. | The [[Negasi nauyi|nauyi]] (lit. weight), with the symbol ₦, is the country's currency. The nauyi is divided into 100 dari. | ||
==Demographics== | |||
Over 88,910,800 people live in Negasi. Approximately half live in urbanized areas with the remainder in rural areas, particularly in northern Negasi's Tumkarik quadrant. | Over 88,910,800 people live in Negasi. Approximately half live in urbanized areas with the remainder in rural areas, particularly in northern Negasi's Tumkarik quadrant. | ||
===Ethnic groups=== | ===Ethnic groups=== | ||
[[Balisubri]] compromise the majority ethnic group in the country. In the west coastal region, a substantial number | [[Balisubri]] compromise the majority ethnic group in the country. In the west coastal region, a substantial number of [[Ithrien]]i can be found. Many [[Auresia]]ns call Elmisi home. The Masokudo quadrant in southern Negasi is home to most of the country's [[Baloma]] population. | ||
===Languages=== | ===Languages=== | ||
Negasi is | {{wp|Hausa language|Negasi}}, the dominant language of the Balisubri, is Negasi's {{wp|official language}}. It is taught in schools alongside various dialects of Liloba in the western, northern, and eastern regions and Koloba in the south. In the cities, Negasi is commonly spoken, but in rural areas, the other languages are often spoken as a person's first language. Many of the dozens of Liloba dialects are mutually intelligible, but not all. In addition to the {{wp|indigenous language}}s, Auresian remains from the colonial era as a minority language. While it can sometimes be heard as a spoken language, it appears most commonly in business and legal documents, usually as a holdover from the colonial era since those usages are becoming less common. While Auresian is not a required language subject in schools, it is taught where there are significant numbers of Auresian minorities, especially in the east, such as the Elmisi region. | ||
===Largest cities=== | ===Largest cities=== | ||
Elmisi is the country's largest city. Located in the Tsaunuka quadrant, Elmisi sits astride the mouth of the Babukar River and eastern entrance to the Ubani Canal | Elmisi is the country's largest city. Located in the Tsaunuka quadrant, Elmisi sits astride the mouth of the Babukar River and eastern entrance to the [[Ubani Canal]]. Negasi's capital and second largest city is [[Bogaye]]. It is located in the Bakin-kogi quadrant on the Dassi Bay and the Ubani Canal's western terminus. | ||
===Religions=== | ===Religions=== | ||
| Line 117: | Line 120: | ||
Education in Negasi is compulsory from age 5 until age 16. The quality of schools in the cities is generally good while rural areas have fewer resources available to support schooling. Negasi Republic University, with campuses in Bogaye and Elmisi, provides higher education at the undergraduate and post-graduate levels. | Education in Negasi is compulsory from age 5 until age 16. The quality of schools in the cities is generally good while rural areas have fewer resources available to support schooling. Negasi Republic University, with campuses in Bogaye and Elmisi, provides higher education at the undergraduate and post-graduate levels. | ||
[[Category:Negasi| ]][[Category:Countries]][[Category:Tharna]][[Category:Tzeraka]] | {{Negasi topics}} | ||
[[Category:Negasi| ]][[Category:Countries]][[Category:Countries in Tharna]][[Category:Countries in Tzeraka]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:27, 19 January 2025
| Negasi Republic Jamhuriyar Negasi (Negasi) | |
| Flag | Coat of arms |
|---|---|

|

|
| Motto: Diligence fosters success (Kwazo yana karfafa nasara) | |
| Anthem: Our Beautiful Homeland (Kyawawan Qasarmu) | |
| Locator map | |
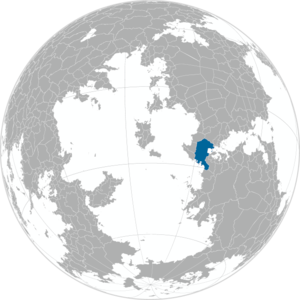
| |
| Capital city | Bogaye |
| Largest city | Elmisi |
| Official language | Negasi |
| Other languages | Liloba, Koloba, Auresian |
| Ethnic group | Balisubri, Baloma |
| Religion | Naskel, Anur |
| Demonym(s) | Negasi |
| Government | |
| Government Type | Unitary parliamentary semi-presidential republic |
| Grand Chief | Rakanja Sadaka |
| Superintendent | Ayubu Owethu |
| Legislature | Superior Council |
| Establishment | |
| Independence | January 30, 7634 |
| Area | |
| Total | 1,217,757.05 km2 |
| Water % | 4.39 |
| Population | |
| Total | 88,910,846 |
| Density | 73.01/km2 |
| Economy | |
| Economy type | Market capitalism |
| GDP (total) | Ꞡ 667.01 billion |
| GDP per capita | Ꞡ 7,614.49 |
| Currency | Negasi nauyi () |
| Other information | |
| Time zone | +3 |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet code | .neg |
Negasi, officially the Negasi Republic (Negasi: Jamhuriyar Negasi), is a country predominantly in southwest Tharna with a portion in northwest Tzeraka. Its western boundary is the Vovodaran Sea and the Tanga Moji Sea lies to the country's east. The Ubani Canal links these two seas, forming a route for ocean-going vessels between the Ovestan and Phasian Oceans. The country has an area of 1,217,757 km2 (470,176 sq mi) with a population of 88,910,846.
History
- Main article: History of Negasi
Early history
Four Councils period
Colonial period
The region was colonized by Auresia in the early 7400s, with the first records of the South Tharnan colony dating from October 5, 7407.
During the colonial period, the Ubani Canal was built. Construction began in 7563 and the canal opened to ship traffic on December 15, 7607 after some delays during the Wolgos Scourge.
Contemporary period
Rising anti-colonialism globally after the turn of the 77th century led to a rise in Negasi nationalism in the 7600s. The formation of the Open Seas Security Organization (OSSO), with its purpose of fostering maritime trade, after the First Coalition War (7632-7634) underscored the importance of the canal for shipping and as a national resource. A general strike occurred across much of Negasi beginning on November 16, 7633. Among other effects, the strike shut down canal operations, preventing ship transit between the Ovestan and Phasian Oceans. The strike led to Auresia granting Negasi its independence on January 30, 7634 in exchange for the restarting of canal operations and a promise to keep the canal open.
In 7672, Negasi expropriated the Ubani Canal from its foreign, private owners and nationalized it, placing it under the jurisdiction of the Ubani Canal Operations Commission, a government corporation.
Geography
While predominantly located in Tharna, Negasi is astride the division between Tharna and Tzeraka, with a portion of the country's southwest located in the latter continent. The Vovodaran Sea lies to the west and the Tanga Moji Sea adjoins Negasi's east coast. The Koradum Mountains lie along a significant portion of Negasi's northwestern border. This region, the Negasi highlands, comprises nearly a third of Negasi's area and is home to three large lakes: Moto, Jelwa, and Tila. The Giganum Mountains are in the south. The Ubani Narrows lies between the two large mountain ranges.
The Oluwa Islands comprise a series of several islands off Negasi's west coast in the Vovodaran. There are several islands in the Tanga Moji, including Jabar, Set, Moriba, Salanko, M’basso, Torosso, Kolibelo, and Dyalinko islands.
Waterways
- See also: Ubani Canal
Over 500 rivers course through Negasi and many serve as sources of hydroelectric power. While most have limited navigability, a few are navigable. In particular, the Babukar River is suitable for ocean-going vessels for nearly a hundred kilometers, and even further with dredging. As a result, the river is the primary waterway for the Ubani Canal which was constructed during the latter half of the 76th century. The canal's total route is 816 km (507 mi), connecting the Ovestan Sea to the Phasian Ocean, using the Ouahika River for the canal's western-most segment.
At over 684 km (425 mi), the Babukar is Negasi's longest river. It is navigable for about two-thirds of its length, with the Ubani Canal route using the river for 338 km (210 mi). The western portion of the canal route uses 196 km (122 mi) of the Ouahika River. The Déda, which flows into the Babukar, shares 149 km (92.6 mi) of its 256 km (159 mi) with the canal. Other significant rivers include the Effingo, Nyale, Sassasam, Missiam, Télo, Sary, N'goulabéri, Ababéri, Cana, and Wukari. Although each is navigable for portions of their course, they are not navigable by ocean-going vessels.
Climate
Negasi has a tropical wet climate along its western coastal region which large humid tropical areas inland. A band of tropical savanna wraps round a region of hot semi-arid grasslands in the east. A small area of oceanic climate lies north of the Giganum Mountains in the south center of the country.
Politics
- Main article: Government of Negasi
The Negasi Republic is a unitary parliamentary semi-presidential republic. The head of state is the grand chief who is chosen by direct election to fill a five-year term. The superintendent is the head of government and is typically the leader of the majority party in the Superior Council, Negasi's parliament. The superintendent serves until removal through a vote of no confidence or another party becomes the majority party in the Superior Council. Rakanja Sadaka serves as grand chief and Ayubu Owethu is the current superintendent.
All citizens aged 18 and over are entitled to vote in all elections. National elections for the grand chief take place every five years and annually for one-fifth (120) of the seats in the Superior Council. Superior councilors are elected on a proportional basis in fixed electoral districts. Each of the 600 superior councilors represents about 148,185 citizens.
Foreign relations
Negasi welcomes diplomatic relations and fair trade with all countries. It is a member of the International Council of Nations, Open Seas Security Organization, and Restoration Coalition.
Military
- Main article: Negasi National Guard
The Negasi National Guard serves as the country's armed forces. It has a land guard, maritime guard, and an air service. The full-time professional force is relatively small but all citizens through age 30 are considered reserves and may be called up in the event of a national emergency.
Administrative divisions
Negasi is a unitary state, so its administrative divisions have limited authorities of their own. The first-level divisions are the four quadrants: Bakin-kogi, Tsaunuka, Tumkarik, and Masokudo. Each is overseen by a high chief and high council. Each quadrant has a number of kasashe (lit. lands) of which there are a total of 96. A chief and council preside over the functions of the kasa. Considered on an equal level, cities, towns, and villages represent local governance under the administration of their local chief and local council. The chiefs at each level are appointed by the chief and confirmed by the council of the next higher level. Citizens directly elect members of the local council. The local councils in turn elect the members of the council in each kasa. The kasa councils elect members of the high council.
Economy
The Ubani Canal is a significant contributor Negasi's economy in terms of both revenues and employment. In addition to the canal itself are a number of related economic activities, including anchoring and mooring, dry docking and ship repair, ship breaking, ship chandlery, and pilotage. In addition, the ports at each end of the canal also offer docking, warehousing, and container terminals.
After the canal, light industrial, particularly textiles, comprises a large segment of the economy. While the country has some heavy industry, it supports the domestic economy and canal activities more so than being an appreciable source of exports. The country's deposits in copper and molybdenun provide for a resource extraction sector, along with the smaller deposits of lead, gold, and cobalt. Negasi has an abundance of limestone and granite, with notable sandstone and marble availability as well. The country has enough salt to provide for a small export market. Negasi's timber industry once supported shipbuilding, but the advent of steel ships has resulted in the demise of shipbuilding and lumber as notable components of the economy. The agricultural sector is large enough to fulfill the majority of Negasi's food needs, with crops and fishing being major components.
Thermal, hydro, wind, and solar provide the bulk of Negasi's electric energy needs. While the country has exploitable natural gas fields, they are not large and have been allocated primarily to supporting the heavy industry sector.
The nauyi (lit. weight), with the symbol ₦, is the country's currency. The nauyi is divided into 100 dari.
Demographics
Over 88,910,800 people live in Negasi. Approximately half live in urbanized areas with the remainder in rural areas, particularly in northern Negasi's Tumkarik quadrant.
Ethnic groups
Balisubri compromise the majority ethnic group in the country. In the west coastal region, a substantial number of Ithrieni can be found. Many Auresians call Elmisi home. The Masokudo quadrant in southern Negasi is home to most of the country's Baloma population.
Languages
Negasi, the dominant language of the Balisubri, is Negasi's official language. It is taught in schools alongside various dialects of Liloba in the western, northern, and eastern regions and Koloba in the south. In the cities, Negasi is commonly spoken, but in rural areas, the other languages are often spoken as a person's first language. Many of the dozens of Liloba dialects are mutually intelligible, but not all. In addition to the indigenous languages, Auresian remains from the colonial era as a minority language. While it can sometimes be heard as a spoken language, it appears most commonly in business and legal documents, usually as a holdover from the colonial era since those usages are becoming less common. While Auresian is not a required language subject in schools, it is taught where there are significant numbers of Auresian minorities, especially in the east, such as the Elmisi region.
Largest cities
Elmisi is the country's largest city. Located in the Tsaunuka quadrant, Elmisi sits astride the mouth of the Babukar River and eastern entrance to the Ubani Canal. Negasi's capital and second largest city is Bogaye. It is located in the Bakin-kogi quadrant on the Dassi Bay and the Ubani Canal's western terminus.
Religions
Naskel is the largest religion in the country with approximately 73,350,000 adherents. Just over 11 million people profess Anur as their religion. Beyond some minor religions, most of the remainder of the country are irreligious.
Education
Education in Negasi is compulsory from age 5 until age 16. The quality of schools in the cities is generally good while rural areas have fewer resources available to support schooling. Negasi Republic University, with campuses in Bogaye and Elmisi, provides higher education at the undergraduate and post-graduate levels.
| Negasi articles | |||
| History | Timeline • Early history • Four Councils • Colonial period • Contemporary Negasi | 
| |
| Geography | Cities • Kasashe • Negasi highlands • Ubani Canal | ||
| Politics | Government • Grand Chief • Military • Police • Superintendent • Superior Council | ||
| Economy | Currency • Energy • Forestry • Mining • Transport (Ubani Canal) | ||
| Society | Symbols | ||
| Category | |||